
Tax Planning
Tax Planning refers to the process of analyzing your financial situation to ensure tax efficiency. It involves utilizing all available deductions, credits, exemptions, and allowances to minimize tax liability while staying compliant with tax laws. Effective tax planning helps individuals and businesses save money, optimize investments, and achieve long-term financial goals.
Key Objectives of Tax Planning
Maximize Savings
- Allocate funds efficiently to save more after taxes
Ensure Compliance
- Avoid penalties by adhering to tax laws and regulations
Plan for the Future
- Create a strategy for long-term financial stability and retirement
Minimize Tax Liability
Reduce the amount of tax payable by leveraging legal provisions.
Tax Planning Strategies
Utilize Deductions and Credits:
Claim deductions for expenses like home loans, education, charity, or medical costs.
Use tax credits for education, energy-efficient upgrades, or child care.
Income Splitting:
Distribute income among family members to lower the overall tax burden.
Tax-Loss Harvesting:
Offset capital gains by selling underperforming investments.
Plan for Retirement:
Contribute to retirement accounts to reduce taxable income and grow savings tax-free.
Business Expenses:
For businesses, deduct expenses like salaries, rent, and equipment purchases

Understanding Tax Planning
Tax planning covers several considerations. Considerations include timing of income, size, and timing of purchases, and planning for other expenditures. Also, the selection of investments and types of retirement plans must complement the tax filing status and deductions to create the best possible outcome.
Investment Planning
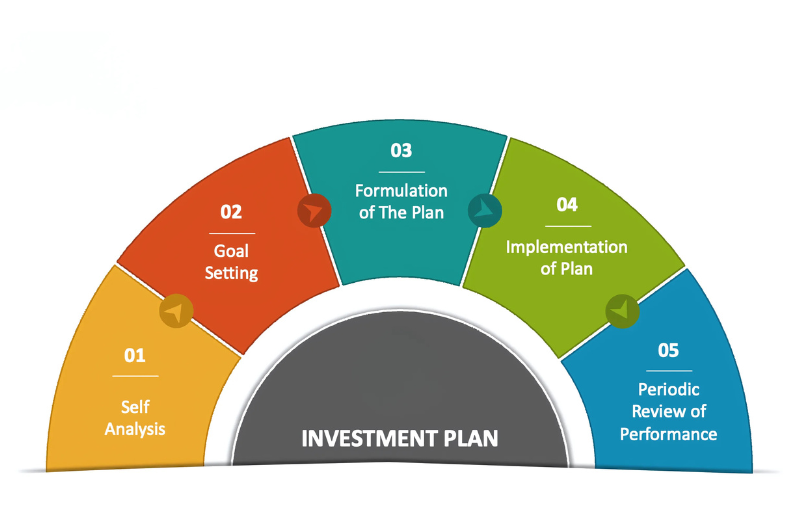
What is Investment planning ?
Investment Planning refers to the process of setting financial goals, assessing resources, and creating a strategy to grow wealth over time. It involves making informed decisions about where and how to allocate funds to achieve long-term financial stability and meet specific objectives, such as retirement, education, or wealth accumulation.
Key Components of Investment Planning
Investment Options
- Bonds, Mutual Funds/ETFs, Real Estate, Commodities, Retirement Accounts
Tax Efficiency
- Optimize investments to minimize tax liabilities (e.g., tax-free bonds, tax-deferred accounts)
Emergency Fund
- Set aside liquid funds for unexpected expenses to avoid disrupting your investment plan
Risk Assessment
Evaluate your risk tolerance (conservative, moderate, or aggressive) based on your financial situation, age, and goals
Frequently Asked Questions...
Can I file taxes online?
Yes, you can file taxes online using IRS-approved software or platforms like TurboTax for convenience.
Who needs to file a tax return?
You must file a tax return if your income exceeds the IRS threshold based on filing status and age.
How long should I keep tax records?
It allows businesses to borrow funds up to a limit, repay, and borrow again as needed.

